
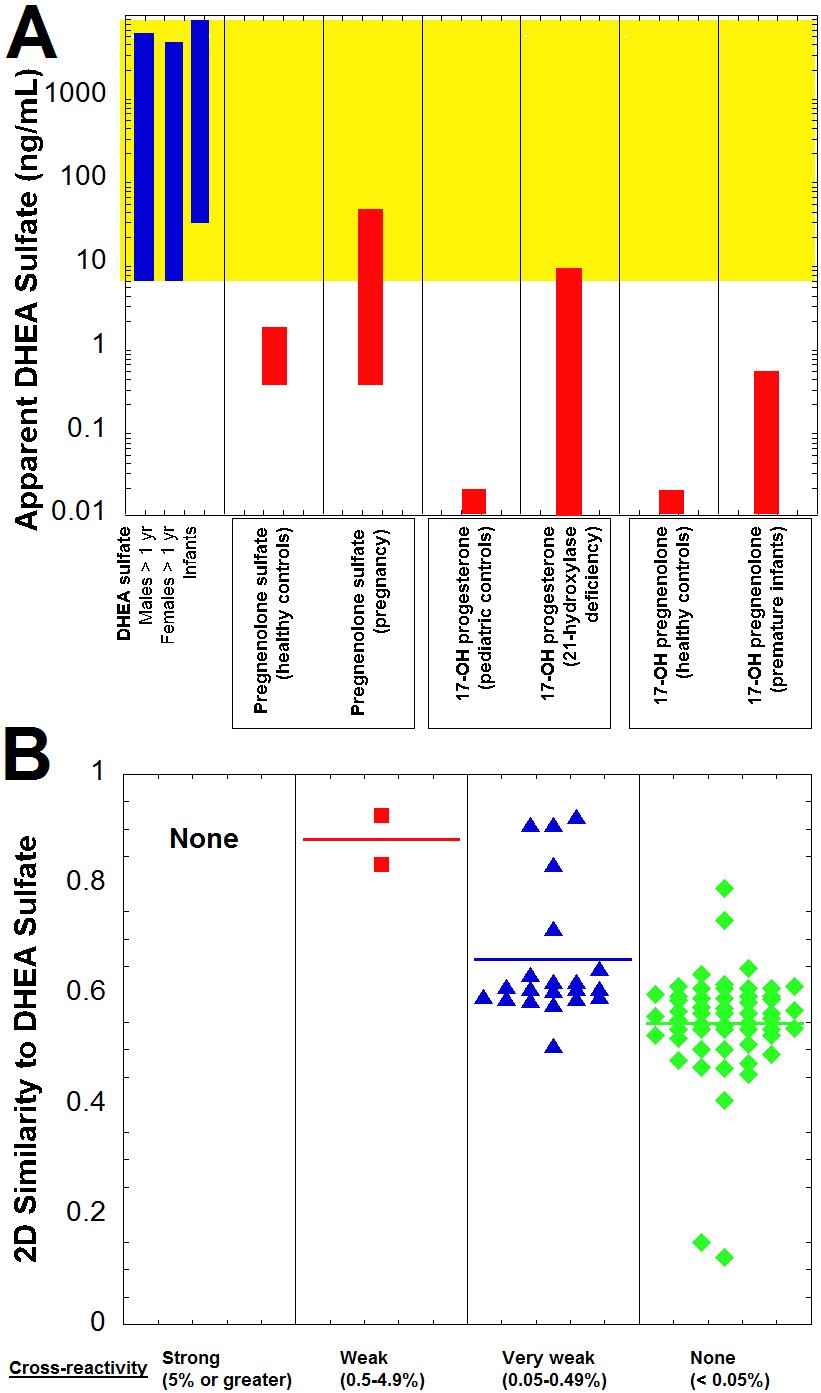
A modified classification is thus proposed. Corticosteroid classes: A quick reference guide including patch test substances and cross-reactivity. Two patient profiles with probably different areas of immune recognition are identified as follows: the profile 1 patients were allergic to the frequently positively reacting cluster 1 only, for whom electrostatic fields (molecular charge) seem important the profile 2 patients reacted to clusters 1 and 2 and/or 3, for whom steric fields (structure) are determinant and who probably presented a global recognition of the corticosteroid skeleton. The purpose of corticosteroid premedication is to mitigate the likelihood of. Among the different interference types, cross-reactivity is more or less foreseeable. Major corticosteroids in Class A include cortisone, hydrocortisone, methylprednisolone, prednisolone, and prednisone. backs such as the low specificity of direct steroid immunoas. The classification obtained after in silico hydrolysis of C(21) and C(17) esters was selected with an optimal cut into three clusters: the patients who reacted positively to cluster 2 (halogenated molecules from group B, with C(16)/C(17) cis ketal or diol structure) and cluster 3 (halogenated molecules from groups C and D1, C(16)-methylated) also reacted to cluster 1 (molecules mostly from groups A and D2, without C(16)-methyl substitution or halogenation and budesonide). There is no cross-reactivity between different classes of contrast medium. There are essentially four classes of corticosteroids: Class A, hydrocortisone-type, Class B, triamcinolone acetonide type, Class C, betamethasone type, and Class D, hydrocortisone-17-butyrate and clobetasone-17-butyrate type. If you have more questions on cross reactivity please contact our customer service center to be connected with our botanist.
This guide illustrates the cross reactive qualities of some grasses, weeds, and trees from the HollisterStier pollen allergen lines. The patch-test results obtained with 66 corticosteroid molecules in 315 previously sensitized subjects were analysed and correlated with modelling and clustering in function of the electrostatic and steric fields of these molecules. RESOURCES CROSS-REACTIVITY GUIDE Grasses. This study compares molecular modelling and patch-test results to determine cross-reactivity patterns. Recent data indicate that C(16)-methylated and nonmethylated molecules need to be distinguished, the latter selectively binding with arginine to form stable cyclic adducts and producing considerably more positive reactions than the former. Corticosteroids have been classified into following four cross-reacting groups in function of their contact-allergenic properties: A, B, C and D, the last subdivided into D1 and D2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
